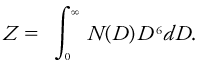Radar reflectivity factor: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
imported>Bcrose |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<div class="term"> | <div class="term"> | ||
== radar reflectivity factor == | == radar reflectivity factor == | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">A quantity determined by the [[drop-size distribution]] of [[precipitation]], which is proportional to the [[radar reflectivity]] if the precipitation particles are spheres small compared with the [[radar]] wavelength.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">Given the drop-size distribution of a sample of [[rain]], the radar reflectivity factor may be computed by summing the sixth-powers of the diameters of all the drops contained in a unit volume of space. Or, regarding the drop-size distribution ''N''(''D'') as a continuous function of [[drop]] size, the [[reflectivity factor]] ''Z'' may be written as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re9.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re9]]</blockquote></div> For ice-phase precipitation, ''N''(''D'') is the distribution of melted diameters. Conventional units of ''Z'' are mm<sup>6</sup> m<sup>-3</sup> and it is sometimes measured on a [[logarithmic scale]] in units of dB''Z''. The [[equivalent reflectivity factor]] ''Z''<sub>''e''</sub> may be estimated from measurements of the radar reflectivity η of precipitation and is defined by <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re10.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re10]]</blockquote></div> where λ is the radar [[wavelength]] and 0.93 is the [[dielectric factor]] for water. Either the reflectivity factor or the equivalent reflectivity factor is frequently used to estimate [[rainfall rate]] using relationships of the form ''Z'' = ''aR''<sup>''b''</sup>'','' where ''a'' and ''b'' are empirical constants and ''R'' is the rainfall rate. For ''R'' in millimeters per hour and ''Z'' or ''Z''<sub>''e''</sub> in mm<sup>6</sup> m<sup>-3</sup>, values of ''a'' range from 200 to 600 and those of ''b'' range from 1.5 to 2. The particular combination of ''a'' = 200 and ''b'' = 1.6 defines the [[Marshall–Palmer relation]]. <br/>''See'' [[radar equation]].</div><br/> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">A quantity determined by the [[drop-size distribution]] of [[precipitation]], which is proportional to the [[radar reflectivity]] if the precipitation particles are spheres small compared with the [[radar]] wavelength.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">Given the drop-size distribution of a sample of [[rain]], the radar reflectivity factor may be computed by summing the sixth-powers of the diameters of all the drops contained in a unit volume of space. Or, regarding the drop-size distribution ''N''(''D'') as a continuous function of [[drop]] size, the [[reflectivity factor|reflectivity factor]] ''Z'' may be written as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re9.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re9]]</blockquote></div> For ice-phase precipitation, ''N''(''D'') is the distribution of melted diameters. Conventional units of ''Z'' are mm<sup>6</sup> m<sup>-3</sup> and it is sometimes measured on a [[logarithmic scale]] in units of [[Dbz|dB''Z'']]. The [[equivalent reflectivity factor]] ''Z''<sub>''e''</sub> may be estimated from measurements of the radar reflectivity η of precipitation and is defined by <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re10.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re10]]</blockquote></div> where λ is the radar [[wavelength]] and 0.93 is the [[dielectric factor]] for water. Either the reflectivity factor or the equivalent reflectivity factor is frequently used to estimate [[rainfall rate]] using relationships of the form ''Z'' = ''aR''<sup>''b''</sup>'','' where ''a'' and ''b'' are empirical constants and ''R'' is the rainfall rate. For ''R'' in millimeters per hour and ''Z'' or ''Z''<sub>''e''</sub> in mm<sup>6</sup> m<sup>-3</sup>, values of ''a'' range from 200 to 600 and those of ''b'' range from 1.5 to 2. The particular combination of ''a'' = 200 and ''b'' = 1.6 defines the [[Marshall-palmer relation|Marshall–Palmer relation]]. <br/>''See'' [[radar equation]].</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | |||
{{TermIndex}} | {{TermIndex}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:00, 15 February 2017
radar reflectivity factor
A quantity determined by the drop-size distribution of precipitation, which is proportional to the radar reflectivity if the precipitation particles are spheres small compared with the radar wavelength.
Given the drop-size distribution of a sample of rain, the radar reflectivity factor may be computed by summing the sixth-powers of the diameters of all the drops contained in a unit volume of space. Or, regarding the drop-size distribution N(D) as a continuous function of drop size, the reflectivity factor Z may be written as For ice-phase precipitation, N(D) is the distribution of melted diameters. Conventional units of Z are mm6 m-3 and it is sometimes measured on a logarithmic scale in units of dBZ. The equivalent reflectivity factor Ze may be estimated from measurements of the radar reflectivity η of precipitation and is defined by where λ is the radar wavelength and 0.93 is the dielectric factor for water. Either the reflectivity factor or the equivalent reflectivity factor is frequently used to estimate rainfall rate using relationships of the form Z = aRb, where a and b are empirical constants and R is the rainfall rate. For R in millimeters per hour and Z or Ze in mm6 m-3, values of a range from 200 to 600 and those of b range from 1.5 to 2. The particular combination of a = 200 and b = 1.6 defines the Marshall–Palmer relation.
See radar equation.
See radar equation.