Polar vortex: Difference between revisions
imported>Liss45 m (→polar vortex) |
imported>Rbrandt |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== polar vortex == | == polar vortex == | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition"> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The term polar vortex is used to describe several different features in the [[atmosphere]]. It most commonly refers to a planetary-scale mid- to high-latitude circumpolar circulation. There are distinct tropospheric and stratospheric circumpolar vortices. <br/> | ||
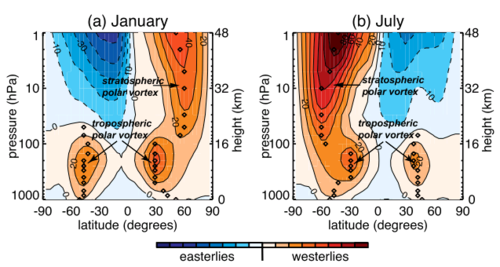
The tropospheric polar vortex is usually defined by [[geopotential]] contours that lie within the core of the tropospheric westerlies (Fraunfeld and Davis 2003). The tropospheric vortex edge is generally between 40º and 50º latitude (Fig. 1), and the vortex exists throughout the year but is strongest during winter when the air within the polar vortex is the coldest. <br/> | |||
The term “polar vortex” is sometimes used in reference to smaller-scale (meso- to [[synoptic]] scale) vortices that usually occur within the tropospheric polar vortex in polar regions near the [[tropopause]]—for example, “tropopause polar vortices (Cavallo and Hakim 2010). <br/> | |||
The stratospheric polar vortex exists from fall to spring and usually extends from just above tropopause to the upper [[stratosphere]] (see Fig. 1). The stratospheric vortex generally increases in size from the lower stratosphere to the upper stratosphere where its edge is located around 50º latitude. The stratospheric vortex breaks down, and the circumpolar flow reverses, during summer (Schoeberl and Hartmann 1991).<br/> | |||
</ | |||
Circumpolar vortices have also been observed on other planetary bodies (e.g., Mars, Venus, Saturn, and Titan) (Read 2011). | |||
<br/> | |||
[[File:PVortex_BAMS_verssion.PNG|500px|center]] | |||
''Term | <blockquote>FIG. 1. Climatological zonal-mean wind in (a) January and (b) July. The diamonds mark the hemispheric maximum of the zonal wind at each pressure level and the approximate edge of the polar vortex for that hemisphere. Data source: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Prediction Center analyses. [Figure is taken from Fig. 2 in Waugh et al. (2017)].</blockquote> | ||
</div><br/> </div> | |||
<p> | |||
Cavallo, S. M., and G. J. Hakim, 2010: Composite structure of tropopause polar cyclones. ''Mon. Wea. Rev.'', '''138''', 3840–3857, doi:10.1175/2010MWR3371.1.<br/> | |||
<br/> | |||
Frauenfeld, O. W., and R. E. Davis, 2003: Northern Hemisphere circumpolar vortex trends and climate change implications. ''J. Geophys. Res.'', '''108''', 4423, doi:10.1029/2002JD002958.<br/> | |||
<br/> | |||
Read, P. L., 2011: Dynamics and circulation regimes of terrestrial planets. ''Planet. Space Sci.'', '''59''', 900–914, doi:10.1016/j.pss.2010.04.024.<br/> | |||
<br/> | |||
Schoeberl, M. R., and D. L. Hartmann 1991, The dynamics of the stratospheric polar vortex and its relation to springtime ozone depletions, ''Science'', '''251''', 46–52<br/> | |||
<br/> | |||
Waugh, D. W., A. H. Sobel, and L. M. Polvani, 2017: What is the polar vortex and how does it influence weather? ''Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc.'', '''98''', 37–44, doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00212.1.</p><br/> | |||
<p>''Term edited 15 March 2019.''</p> | |||
{{TermIndex}} | {{TermIndex}} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:45, 15 March 2019
polar vortex
The tropospheric polar vortex is usually defined by geopotential contours that lie within the core of the tropospheric westerlies (Fraunfeld and Davis 2003). The tropospheric vortex edge is generally between 40º and 50º latitude (Fig. 1), and the vortex exists throughout the year but is strongest during winter when the air within the polar vortex is the coldest.
The term “polar vortex” is sometimes used in reference to smaller-scale (meso- to synoptic scale) vortices that usually occur within the tropospheric polar vortex in polar regions near the tropopause—for example, “tropopause polar vortices (Cavallo and Hakim 2010).
The stratospheric polar vortex exists from fall to spring and usually extends from just above tropopause to the upper stratosphere (see Fig. 1). The stratospheric vortex generally increases in size from the lower stratosphere to the upper stratosphere where its edge is located around 50º latitude. The stratospheric vortex breaks down, and the circumpolar flow reverses, during summer (Schoeberl and Hartmann 1991).
Circumpolar vortices have also been observed on other planetary bodies (e.g., Mars, Venus, Saturn, and Titan) (Read 2011).
FIG. 1. Climatological zonal-mean wind in (a) January and (b) July. The diamonds mark the hemispheric maximum of the zonal wind at each pressure level and the approximate edge of the polar vortex for that hemisphere. Data source: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Prediction Center analyses. [Figure is taken from Fig. 2 in Waugh et al. (2017)].
Cavallo, S. M., and G. J. Hakim, 2010: Composite structure of tropopause polar cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev., 138, 3840–3857, doi:10.1175/2010MWR3371.1.
Frauenfeld, O. W., and R. E. Davis, 2003: Northern Hemisphere circumpolar vortex trends and climate change implications. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4423, doi:10.1029/2002JD002958.
Read, P. L., 2011: Dynamics and circulation regimes of terrestrial planets. Planet. Space Sci., 59, 900–914, doi:10.1016/j.pss.2010.04.024.
Schoeberl, M. R., and D. L. Hartmann 1991, The dynamics of the stratospheric polar vortex and its relation to springtime ozone depletions, Science, 251, 46–52
Waugh, D. W., A. H. Sobel, and L. M. Polvani, 2017: What is the polar vortex and how does it influence weather? Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 98, 37–44, doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00212.1.
Term edited 15 March 2019.