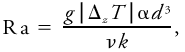Rayleigh number: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot (Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == Rayleigh number == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The nondime...") |
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The nondimensional ratio between the product of [[buoyancy]] forces and heat [[advection]] and the product of [[viscous forces]] and heat [[conduction]] in a fluid.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is written as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re19.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re19]]</blockquote></div> where ''g'' is the [[acceleration of gravity]], Δ<sub>''z''</sub>''T'' a characteristic vertical [[temperature]] difference in the characteristic depth ''d'', α the [[coefficient of expansion]], ν the [[kinematic viscosity]], and ''k'' the molecular [[conductivity]]. The Rayleigh number is equal to the product of the [[Grashoff]] and [[Prandtl numbers]], and is the critical [[parameter]] in the theory of [[thermal instability]] for laboratory flows.</div><br/> </div> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The nondimensional ratio between the product of [[buoyancy]] forces and heat [[advection]] and the product of [[viscous forces]] and heat [[conduction]] in a fluid.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is written as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Re19.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Re19]]</blockquote></div> where ''g'' is the [[acceleration of gravity]], Δ<sub>''z''</sub>''T'' a characteristic vertical [[temperature]] difference in the characteristic depth ''d'', α the [[coefficient of expansion]], ν the [[kinematic viscosity|kinematic viscosity]], and ''k'' the molecular [[conductivity]]. The Rayleigh number is equal to the product of the [[Grashoff number|Grashoff]] and [[Prandtl numbers]], and is the critical [[parameter]] in the theory of [[thermal instability]] for laboratory flows.</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 25 April 2012
Rayleigh number
The nondimensional ratio between the product of buoyancy forces and heat advection and the product of viscous forces and heat conduction in a fluid.
It is written as where g is the acceleration of gravity, ΔzT a characteristic vertical temperature difference in the characteristic depth d, α the coefficient of expansion, ν the kinematic viscosity, and k the molecular conductivity. The Rayleigh number is equal to the product of the Grashoff and Prandtl numbers, and is the critical parameter in the theory of thermal instability for laboratory flows.