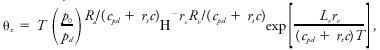Equivalent potential temperature: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot (Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == equivalent potential temperature == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_defini...") |
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">( | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">(''Also called'' [[wet-equivalent potential temperature]].) A thermodynamic quantity, with its natural [[logarithm]] proportional to the [[entropy]] of [[moist air]], that is conserved in a [[reversible moist-adiabatic process|reversible moist adiabatic process]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is given most accurately as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee56.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee56]]</blockquote></div> where θ<sub>''e''</sub> is the equivalent potential temperature, ''c''<sub>''pd''</sub> is the [[heat capacity]] at constant [[pressure]] of [[dry air]], ''r''<sub>''t''</sub> is the [[total water mixing ratio]], ''c'' is the heat capacity of liquid water, ''T'' is the [[temperature]], ''R''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for dry air, ''p''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[partial pressure]] of dry air, ''p''<sub>0</sub> is a reference pressure (usually 100 kPa), ''L''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[latent heat]] of [[vaporization]], ''r''<sub>''v''</sub> is the vapor [[mixing ratio]], ''R''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for [[water vapor]], and Η is the [[relative humidity]]. Neglect of the quantity ''r''<sub>''t''</sub>''c'', where it appears, yields a simpler expression with good [[accuracy]].</div><br/> </div><div class="reference">Paluch, I. 1979. J. Atmos. Sci.. 36. 2467–2478. </div><br/> <div class="reference">Emanuel, K. A. 1994. Atmospheric Convection. Oxford University Press, . 580 pp. </div><br/> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:55, 25 April 2012
equivalent potential temperature
(Also called wet-equivalent potential temperature.) A thermodynamic quantity, with its natural logarithm proportional to the entropy of moist air, that is conserved in a reversible moist adiabatic process.
It is given most accurately as where θe is the equivalent potential temperature, cpd is the heat capacity at constant pressure of dry air, rt is the total water mixing ratio, c is the heat capacity of liquid water, T is the temperature, Rd is the gas constant for dry air, pd is the partial pressure of dry air, p0 is a reference pressure (usually 100 kPa), Lv is the latent heat of vaporization, rv is the vapor mixing ratio, Rv is the gas constant for water vapor, and Η is the relative humidity. Neglect of the quantity rtc, where it appears, yields a simpler expression with good accuracy.
Paluch, I. 1979. J. Atmos. Sci.. 36. 2467–2478.
Emanuel, K. A. 1994. Atmospheric Convection. Oxford University Press, . 580 pp.