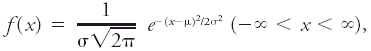Normal distribution: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot (Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == normal distribution == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">(<br/>'...") |
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">( | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">(''Or'' Gaussian distribution.) The [[fundamental frequency]] distribution of [[statistical]] analysis.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">A continuous [[variate]] ''x'' is said to have a normal distribution or to be normally distributed if it possesses a [[density function]] ''f''(''x'') that satisfies the equation <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ne8.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ne8]]</blockquote></div> where μ is the [[arithmetic mean]] (or first [[moment]]) and σ is the [[standard deviation]]. About two- thirds of the total area under the curve is included between ''x'' = μ - σ and ''x'' = μ + σ. The corresponding [[frequency distribution]] of vectors is the [[normal circular distribution]] in which the frequencies of [[vector]] deviations are represented by a series of circles centered on a vector mean. When applied to [[error distribution]], this function is the [[normal law of errors]], and the distribution is called the [[normal curve of error]]. Although discovered by DeMoivre, the normal distribution is usually called the Gaussian distribution. In early anthropometric studies and also investigations of [[random errors]] in physical measurements, the variates exhibited the normal distribution so faithfully that this distribution was mistakenly assumed to be the governing principle of nearly all random phenomena and was therefore given the name "normal." While less universal than formerly believed, the normal distribution does have remarkable breadth of application, inasmuch as the distribution of averages computed from repeated random samples of almost any [[population]] tends more and more nearly toward the "normal" form as the [[sample]] size increases. Formulated in precise terms, this proposition is known as the [[central limit theorem]].</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 14:45, 20 February 2012
normal distribution[edit | edit source]
A continuous variate x is said to have a normal distribution or to be normally distributed if it possesses a density function f(x) that satisfies the equation where μ is the arithmetic mean (or first moment) and σ is the standard deviation. About two- thirds of the total area under the curve is included between x = μ - σ and x = μ + σ. The corresponding frequency distribution of vectors is the normal circular distribution in which the frequencies of vector deviations are represented by a series of circles centered on a vector mean. When applied to error distribution, this function is the normal law of errors, and the distribution is called the normal curve of error. Although discovered by DeMoivre, the normal distribution is usually called the Gaussian distribution. In early anthropometric studies and also investigations of random errors in physical measurements, the variates exhibited the normal distribution so faithfully that this distribution was mistakenly assumed to be the governing principle of nearly all random phenomena and was therefore given the name "normal." While less universal than formerly believed, the normal distribution does have remarkable breadth of application, inasmuch as the distribution of averages computed from repeated random samples of almost any population tends more and more nearly toward the "normal" form as the sample size increases. Formulated in precise terms, this proposition is known as the central limit theorem.