Accumulated cooling: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|Definitions={{Definition | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
|Num=1 | |Num=1 | ||
|Meaning= | |Meaning=The total cooling since the time in the evening when the turbulent [[heat flux]] near the ground produces a net [[heat]] flow from the earth to the [[atmosphere]]; used to measure or predict evolution of the [[stable boundary layer]]. | ||
The total cooling since the time in the evening when the turbulent [[heat flux]] near the ground produces a net [[heat]] flow from the earth to the [[atmosphere]]; used to measure or predict evolution of the [[stable boundary layer]]. | |Explanation=It is defined as the integral of the surface kinematic heat flux [[File:ams2001glos-Aex01.gif|link=|ams2001glos-Aex01]] over time, starting from the time ''t''<sub>0</sub> just before [[sunset]] when the flux changes from positive to negative, and ending at any time ''t''<sub>''e''</sub> before the flux changes sign back to positive. Dimensions are [[temperature]] times length, such as (K·m). In the absence of [[advection]] and direct [[radiative cooling]] of the air, accumulated cooling (AC) also equals the area under the [[potential temperature]] profile ''z''(θ), integrated from the surface potential temperature θ<sub>''s''</sub> to the residual-layer potential temperature θ<sub>''RL''</sub>, that is, <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ae6.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ae6]]</blockquote> | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 13 January 2024
The total cooling since the time in the evening when the turbulent heat flux near the ground produces a net heat flow from the earth to the atmosphere; used to measure or predict evolution of the stable boundary layer.
It is defined as the integral of the surface kinematic heat flux 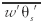 over time, starting from the time t0 just before sunset when the flux changes from positive to negative, and ending at any time te before the flux changes sign back to positive. Dimensions are temperature times length, such as (K·m). In the absence of advection and direct radiative cooling of the air, accumulated cooling (AC) also equals the area under the potential temperature profile z(θ), integrated from the surface potential temperature θs to the residual-layer potential temperature θRL, that is,
over time, starting from the time t0 just before sunset when the flux changes from positive to negative, and ending at any time te before the flux changes sign back to positive. Dimensions are temperature times length, such as (K·m). In the absence of advection and direct radiative cooling of the air, accumulated cooling (AC) also equals the area under the potential temperature profile z(θ), integrated from the surface potential temperature θs to the residual-layer potential temperature θRL, that is,
