Aridity index: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot (Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == aridity index == </div> #<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">As used by C...") |
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
#<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">As used by C. W. Thornthwaite in his 1948 [[climatic classification]]: an index of the degree of [[water deficit]] below [[water need]] at any given station; a measure of [[aridity]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is calculated, independently of the opposite [[humidity index]], as follows: <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ae27.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ae27]]</blockquote></div> where ''d'' (the water deficit) is the sum of the monthly differences between precipitation and [[potential evapotranspiration]] for those months when the [[normal]] precipitation is less than the normal potential evapotranspiration; and where ''n'' is the sum of monthly values of potential evapotranspiration for the deficient months.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">Thornthwaite puts the aridity index to two uses: 1) as a component of the moisture index; 2) as a basis for the more detailed classification of [[moist climates]] (perhumid, humid, and moist subhumid climates).</div><br/> </div> | #<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">As used by C. W. Thornthwaite in his 1948 [[climatic classification]]: an index of the degree of [[water deficit]] below [[water need]] at any given station; a measure of [[aridity]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is calculated, independently of the opposite [[humidity index]], as follows: <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ae27.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ae27]]</blockquote></div> where ''d'' (the water deficit) is the sum of the monthly differences between precipitation and [[potential evapotranspiration|potential evapotranspiration]] for those months when the [[normal]] precipitation is less than the normal potential evapotranspiration; and where ''n'' is the sum of monthly values of potential evapotranspiration for the deficient months.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">Thornthwaite puts the aridity index to two uses: 1) as a component of the moisture index; 2) as a basis for the more detailed classification of [[moist climates]] (perhumid, humid, and moist subhumid climates).</div><br/> </div> | ||
#<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition"><br/>''See'' [[index of aridity]].</div><br/> </div> | #<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition"><br/>''See'' [[index of aridity]].</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 25 April 2012
aridity index[edit | edit source]
- As used by C. W. Thornthwaite in his 1948 climatic classification: an index of the degree of water deficit below water need at any given station; a measure of aridity.
It is calculated, independently of the opposite humidity index, as follows:where d (the water deficit) is the sum of the monthly differences between precipitation and potential evapotranspiration for those months when the normal precipitation is less than the normal potential evapotranspiration; and where n is the sum of monthly values of potential evapotranspiration for the deficient months.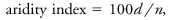
Thornthwaite puts the aridity index to two uses: 1) as a component of the moisture index; 2) as a basis for the more detailed classification of moist climates (perhumid, humid, and moist subhumid climates).
See index of aridity.
