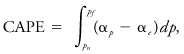Convective available potential energy
From Glossary of Meteorology
convective available potential energy[edit | edit source]
(Abbreviated CAPE.) The maximum energy available to an ascending parcel, according to parcel theory.
On a thermodynamic diagram this is called positive area, and can be seen as the region between the lifted parcel process curve and the environmental sounding, from the parcel's level of free convection to its level of neutral buoyancy. It may be defined as where αe is the environmental specific volume profile, αp is the specific volume of a parcel moving upward moist-adiabatically from the level of free convection, pf is the pressure at the level of free convection, and pn is the pressure at the level of neutral buoyancy. The value depends on whether the moist-adiabatic process is considered reversible or irreversible (conventionally irreversible) and whether the latent heat of freezing is considered (conventionally not).
Compare convective inhibition.
Compare convective inhibition.