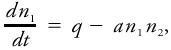Recombination coefficient
From Glossary of Meteorology
recombination coefficient
A measure of the specific rate at which oppositely charged ions join to form neutral particles (a measure of ion recombination).
Mathematically, if q is the ionization rate expressed in terms of ion pairs created per unit volume per unit time, n1 the number of positive small ions per unit volume at time t, and n2 the number of negative small ions per unit volume at the same instant, then the time rate of change in, for example, positive small-ion density is if we ignore effects due to Aitken nuclei and large ions. In this expression a is the recombination coefficient for small ions and is of the order of 10-6 cm3 s-1 at sea level. The recombination coefficient between large and small ions is of the same magnitude; the recombination coefficient for large ions neutralizing large ions is much smaller, of the order of 10-9 cm3 s-1.
See combination coefficient.
See combination coefficient.