Potential temperature
From Glossary of Meteorology
potential temperature
- The temperature that an unsaturated parcel of dry air would have if brought adiabatically and reversibly from its initial state to a standard pressure, p0, typically 100 kPa.
Its mathematical expression iswhere θ is the potential temperature, T is temperature, and κ is the Poisson constant. This exponent is often assumed to be 2/7, the ratio of the gas constant to the specific heat capacity at constant pressure for an ideal diatomic gas.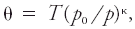
See virtual potential temperature, liquid water potential temperature, equivalent potential temperature, wet-bulb potential temperature.
- In oceanography, the temperature that a water sample would attain if raised adiabatically to the sea surface.
For the deepest points of the ocean, which are just over 10 000 m, the adiabatic cooling would be less than 1.5°C.
