Air
air[edit | edit source]
Mixture of gases forming Earth's atmosphere, consisting of nitrogen (∼78%), oxygen (∼21%), water vapor, and other trace gases such as carbon dioxide, helium, argon, ozone, or various pollutants.
The concentration of water vapor is very variable, being a strong function of temperature and, hence, altitude in the atmosphere. Dry air is referred to as air from which measurable amounts of water vapor have been physically removed. Pure, dry air has a density of 1.293 kg m−3 at a temperature of 273 K and a pressure of 101.325 kPa. Apart from the variability of water vapor, the composition of air is essentially constant to an altitude of at least 50 km and is presently approximated as follows.
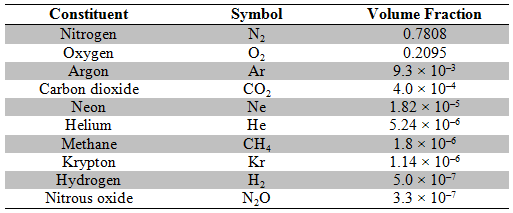
The concentration of ozone is variable, between approximately 10 and 0.01 ppm. Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide have all been increasing since the beginning of the industrial age. Carbon dioxide and methane concentrations vary by season and location.
Term revised 26 June 2017.
