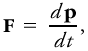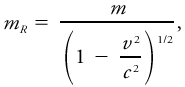Rest mass
From Glossary of Meteorology
rest mass
(Also called proper mass, invariant mass, velocity-independent mass.) The mass of an object measured in a coordinate system in which the object is at rest.
To retain within special relativity the classical form of Newton's dynamical law of motion for a body with momentum p and velocity v acted upon by a force F momentum may be written as The relativistic mass is defined as where m is the rest mass and c is the free-space speed of light. For meteorological applications, rest mass and relativistic mass are so nearly identical that it is largely pointless to make a distinction between the two.
Helliwell, T. M. 1966. Introduction to Special Relativity. 148–150.