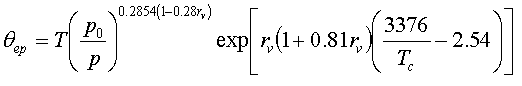Pseudoequivalent potential temperature
From Glossary of Meteorology
pseudoequivalent potential temperature
The temperature a sample of air would have if it were expanded by a pseudoadiabatic process to zero pressure and then compressed to a reference pressure of 100 kPa by a dry-adiabatic process.
This quantity is conserved in a pseudoadiabatic process and is given approximately by where T is the temperature, p is the pressure, Tc is the condensation temperature (obtainable from the dewpoint formula) and rv is the water vapor mixing ratio. When rv = 0, θep = θ, the potential temperature.
Bolton, D. 1980. The computation of equivalent potential temperature. Mon. Wea. Rev.. 108. 1046–1053.