Orthogonal
From Glossary of Meteorology
orthogonal
- Originally, at right angles; later generalized to mean the vanishing of a sum (or integral) of products.
The cosine of the angle between two vectors, V1 and V2 with respective components, (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2), is proportional to the sum of products, x1x2 + y1y2 + z1z2. Hence, if the vectors are perpendicular, the latter sum equals zero. For this reason any two series of numbers, (x1, x2, · · ·, xn) and (y1, y2, · · ·, yn) is said to be orthogonal if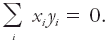
See orthogonal functions.
- On an ocean-wave refraction diagram, a ray drawn everywhere at right angles to wave crests.
