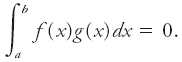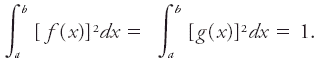Orthogonal functions
From Glossary of Meteorology
orthogonal functions
A set of functions, any two of which, by analogy to orthogonal vectors, vanish if their product is summed by integration over a specified interval.
For example, f(x) and g(x) are orthogonal in the interval x = a to x = b if The functions are also said to be normal if The most familiar examples of such functions, many of which have great importance in mathematical physics, are the sine and cosine functions between zero and 2π.