adiabatic lapse rate
The rate of decrease in temperature with height via an adiabatic process.
- Dry-adiabatic lapse rate A process lapse rate of temperature, the rate of decrease of temperature with height of a parcel of dry air lifted by a reversible adiabatic process through an atmosphere in hydrostatic equilibrium. This lapse rate is g/cpd, where g is the gravitational acceleration and cpd is the specific heat of dry air at constant pressure, approximately 9.8°C km−1. Potential temperature is constant with height in an atmospheric layer with this lapse rate.
- Moist-unsaturated adiabatic lapse rate The adiabatic lapse rate of unsaturated air containing water vapor. This differs from definition 1 by the factor
where rv is the mixing ratio of water vapor and cpv is the specific heat of water vapor.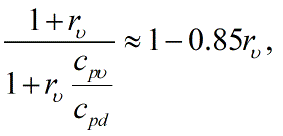
- Moist-adiabatic lapse rate (or saturation-adiabatic lapse rate or moist-saturated adiabatic lapse rate) The rate of decrease of temperature with height along a moist adiabat. It is given approximately by Γm in the following:
where g is the gravitational acceleration, cpd is the specific heat at constant pressure of dry air, rv is the mixing ratio of water vapor, Lv is the latent heat of vaporization, R is the gas constant for dry air, ϵ is the ratio of the gas constants for dry air and water vapor, and T is temperature. This expression is an approximation for both the reversible moist-adiabatic lapse rate and the pseudoadiabatic lapse rate, with more accurate expressions given under those definitions. When most of the condensed water is frozen, this may be replaced by a similar expression but with Lv replaced by the latent heat of sublimation.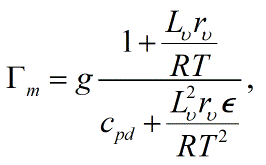
Term edited 16 August 2021.
