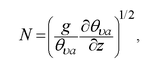Brunt-väisälä frequency: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Liss45 |
imported>Liss45 |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The [[frequency]] ''N'' at which a displaced [[air parcel]] will oscillate when displaced vertically within a [[static stability|statically stable]] environment.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is given as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:Brunt_V_final.png|150px|center]]</blockquote></div> where ''g'' = 9.8 m s<sup> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The [[frequency]] ''N'' at which a displaced [[air parcel]] will oscillate when displaced vertically within a [[static stability|statically stable]] environment.</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is given as <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:Brunt_V_final.png|150px|center]]</blockquote></div> where ''g'' = 9.8 m s<sup>–1</sup> is gravitational [[acceleration]], ''θ''<sub>''υa''</sub> is the ambient virtual potential temperature, and ∂''θ''<sub>''υa''</sub>/∂''z'' is the vertical [[gradient]] of the ambient [[virtual potential temperature]]. Units are radians per second, although this is usually abbreviated as s<sup>–1</sup>. This frequency is not defined in statically [[unstable air]] and is zero in statically neutral air. The frequency of internal [[gravity waves]] in the [[atmosphere]] cannot exceed the local Brunt–Väisälä frequency. This frequency is also sometimes used as a measure of the [[stability]] within a statically stable environment.</div><br/> </div> | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition"><br/>''See also'' [[buoyancy frequency]].</div><br/>Reference:</div><div class="reference">Stull, R. B. 1995. Meteorology Today for Scientists and Engineers. 385 pp. </div><br/> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition"><br/>''See also'' [[buoyancy frequency]].</div><br/>Reference:</div><div class="reference">Stull, R. B. 1995. Meteorology Today for Scientists and Engineers. 385 pp. </div><br/> | ||
Revision as of 11:37, 15 December 2014
Brunt–Väisälä frequency
The frequency N at which a displaced air parcel will oscillate when displaced vertically within a statically stable environment.
It is given as where g = 9.8 m s–1 is gravitational acceleration, θυa is the ambient virtual potential temperature, and ∂θυa/∂z is the vertical gradient of the ambient virtual potential temperature. Units are radians per second, although this is usually abbreviated as s–1. This frequency is not defined in statically unstable air and is zero in statically neutral air. The frequency of internal gravity waves in the atmosphere cannot exceed the local Brunt–Väisälä frequency. This frequency is also sometimes used as a measure of the stability within a statically stable environment.
See also buoyancy frequency.
Reference:
Stull, R. B. 1995. Meteorology Today for Scientists and Engineers. 385 pp.
term edited 15 Dec 2014