Gradient
From Glossary of Meteorology
gradient[edit | edit source]
- The space rate of decrease of a function.
The gradient of a function in three space dimensions is the vector normal to surfaces of constant value of the function and directed toward decreasing values, with magnitude equal to the rate of decrease of the function in this direction. The gradient of a function f is denoted by -∇f (without the minus sign in the older literature) and is itself a function of both space and time. The ascendent is the negative of the gradient. In Cartesian coordinates, the expression for the gradient isFor expressions in other coordinate systems, see Berry et al. (1945).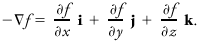
- Often loosely used to denote the magnitude of the gradient or ascendent (i.e., without regard to sign) of a horizontal pressure field.
Berry, F. A., E. Bollay, and N. Beers 1945. Handbook of Meteorology. 224–225.
