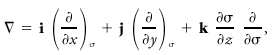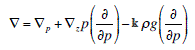Del operator: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
imported>Bcrose |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<div class="term"> | <div class="term"> | ||
== del operator == | == del operator == | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The [[operator]] (written '''∇''') used to transform a [[scalar]] field into the [[ascendent]] (the negative of the [[gradient]]) of that [[field]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">In [[Cartesian coordinates]] the three-dimensional del operator is <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De16.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De16]]</blockquote></div> and the horizontal component is <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De17.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De17]]</blockquote></div> Expressions for '''∇''' in various systems of [[curvilinear coordinates]] may be found in any textbook | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">The [[operator]] (written '''∇''') is used to transform a [[scalar]] field into the [[ascendent]] (the negative of the [[gradient]]) of that [[field]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">In [[Cartesian coordinates]] the three-dimensional del operator is <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De16.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De16]]</blockquote></div> and the horizontal component is <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De17.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De17]]</blockquote></div> Expressions for '''∇''' in various systems of [[curvilinear coordinates]] may be found in any textbook of [[vector]] analysis. In meteorology it is often convenient to use a [[thermodynamic function of state|thermodynamic function of state]], such as [[pressure]] or [[potential temperature]], as the vertical coordinate. If the chosen function is σ, then <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De18.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De18]]</blockquote></div> where differentiation with respect to ''x'' and ''y'' is understood as carried out on surfaces of constant σ (the subscript usually being omitted). The horizontal component is now <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De19.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De19]]</blockquote></div> If the [[quasi-hydrostatic approximation]] is justified, as in most meteorological contexts, pressure is a useful coordinate, and <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De20_revised.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De20_revised]]</blockquote></div> where ''g'' is the [[acceleration of gravity]] and ρ is the [[density]]. Here <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-De21.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-De21]]</blockquote></div> with differentiation carried out in [[isobaric surfaces]], and '''∇'''<sub>''z''</sub> is the horizontal gradient operator in Cartesian-altitude coordinates.</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | |||
<p>''Term updated 8 March 2017.''</p> | |||
{{TermIndex}} | {{TermIndex}} | ||
{{TermFooter}} | {{TermFooter}} | ||
[[Category:Terms_D]] | [[Category:Terms_D]] | ||
Revision as of 11:56, 8 March 2017
del operator[edit | edit source]
The operator (written ∇) is used to transform a scalar field into the ascendent (the negative of the gradient) of that field.
In Cartesian coordinates the three-dimensional del operator is and the horizontal component is Expressions for ∇ in various systems of curvilinear coordinates may be found in any textbook of vector analysis. In meteorology it is often convenient to use a thermodynamic function of state, such as pressure or potential temperature, as the vertical coordinate. If the chosen function is σ, then where differentiation with respect to x and y is understood as carried out on surfaces of constant σ (the subscript usually being omitted). The horizontal component is now If the quasi-hydrostatic approximation is justified, as in most meteorological contexts, pressure is a useful coordinate, and where g is the acceleration of gravity and ρ is the density. Here with differentiation carried out in isobaric surfaces, and ∇z is the horizontal gradient operator in Cartesian-altitude coordinates.
Term updated 8 March 2017.