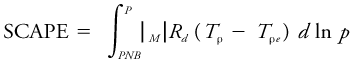Slantwise convective available potential energy: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
imported>Perlwikibot (Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == slantwise convective available potential energy == </div> <div class="definition"><div clas...") |
imported>Perlwikibot No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">(Abbreviated SCAPE.) The total amount of [[potential energy]] available for conversion into [[kinetic energy]] in the slantwise-upward displacement of a particular sample of air in an [[atmosphere]] that is unstable to [[slantwise convection]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is given by <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Se33.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Se33]]</blockquote></div> where ''R''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for [[dry air]]; ''T''<sub>ρ</sub> is the [[density temperature]] of the sample in question, lifted to a [[pressure]] ''p'' by a reversible [[adiabatic process]]; ''T''<sub>ρ''e''</sub> is the density temperature of the [[environment]] through which the sample is lifted, ''PNB'' is the pressure at which the lifted sample has the same density temperature as its environment; and <div class="inline-formula">[[File:ams2001glos-Sex05.gif|link=|ams2001glos-Sex05]]</div> denotes that the sample should be lifted slantwise along a surface of constant [[absolute momentum]], or, in circularly symmetric flows such as [[tropical cyclones]], constant [[angular momentum]].</div><br/> </div> | <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">(Abbreviated SCAPE.) The total amount of [[potential energy|potential energy]] available for conversion into [[kinetic energy]] in the slantwise-upward displacement of a particular sample of air in an [[atmosphere]] that is unstable to [[slantwise convection]].</div><br/> <div class="paragraph">It is given by <div class="display-formula"><blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Se33.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Se33]]</blockquote></div> where ''R''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for [[dry air]]; ''T''<sub>ρ</sub> is the [[density temperature]] of the sample in question, lifted to a [[pressure]] ''p'' by a reversible [[adiabatic process]]; ''T''<sub>ρ''e''</sub> is the density temperature of the [[environment]] through which the sample is lifted, ''PNB'' is the pressure at which the lifted sample has the same density temperature as its environment; and <div class="inline-formula">[[File:ams2001glos-Sex05.gif|link=|ams2001glos-Sex05]]</div> denotes that the sample should be lifted slantwise along a surface of constant [[absolute momentum]], or, in circularly symmetric flows such as [[tropical cyclones]], constant [[angular momentum]].</div><br/> </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 25 April 2012
slantwise convective available potential energy[edit | edit source]
(Abbreviated SCAPE.) The total amount of potential energy available for conversion into kinetic energy in the slantwise-upward displacement of a particular sample of air in an atmosphere that is unstable to slantwise convection.
It is given by where Rd is the gas constant for dry air; Tρ is the density temperature of the sample in question, lifted to a pressure p by a reversible adiabatic process; Tρe is the density temperature of the environment through which the sample is lifted, PNB is the pressure at which the lifted sample has the same density temperature as its environment; and  denotes that the sample should be lifted slantwise along a surface of constant absolute momentum, or, in circularly symmetric flows such as tropical cyclones, constant angular momentum.
denotes that the sample should be lifted slantwise along a surface of constant absolute momentum, or, in circularly symmetric flows such as tropical cyclones, constant angular momentum.