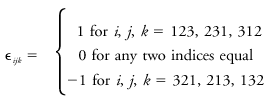alternating unit tensor
From Glossary of Meteorology
A mathematical function with symbol εijk defined to switch between the discrete values of +1, 0, and -1, depending on the values of the three indices i, j, and k:
Stull, R. B. 1988. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology. 666 pp.
It is one of the tools used in Einstein's summation notation to handle operations equivalent to cross products in vector notation. For example: A × B = εijkAiBjδk, where Ai and Bj represent vectors in summation notation, and δk is the unit vector. Subscripts or indices i, j, and k must each take on the values of 1, 2, and 3, representing the Cartesian directions of x, y, and z. The alternating unit tensor is useful to describe the Coriolis term in the equations of motion: ∂Ui/ ∂t = . . . + fεij3Uj + . . ., where f is the Coriolis parameter, Ui and Uj are wind components, and t is time. Summation notation is commonly used in atmospheric turbulence studies.
Stull, R. B. 1988. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology. 666 pp.