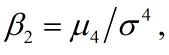kurtosis
A measure of the heaviness (remoteness and mass) of the tails of a probability distribution. It is defined as
where μ4 is the fourth (statistical) moment about the mean and σ2 the variance. For the normal distribution, β2 = 3; cases for which β2 > 3 indicate distributions that are more outlier-prone (i.e., have heavier tails) than the normal (Gaussian) distribution, while those for which β2 < 3 indicate distributions that are less outlier-prone than the normal. In particular, the rectangular distribution f(x) = 1 (0 < x < 1) has β2 = 1.8. The terms leptokurtic, mesokurtic, and platykurtic refer to curves for which the values of β2 are, respectively, greater than 3, equal to 3, and less than 3. Excess is a relative expression for kurtosis, and the coefficient of excess γ2 is defined as β2 − 3. For more information about correct and incorrect interpretations of kurtosis, see Westfall (2014).
Term edited 15 March 2019.