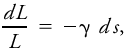Rain attenuation
From Glossary of Meteorology
rain attenuation[edit | edit source]
The depletion of electromagnetic energy during propagation through rain, caused by raindrop scattering and absorption.
The effect is described by Beer's law as the fractional depletion of radiance per unit pathlength, where L is the monochromatic radiance at a given wavelength, γ is the volume attenuation coefficient (or extinction coefficient) due to absorption and scattering by rain, and ds is an increment of pathlength. In radar, the depletion of power from incident plane-wave radiation is sometimes described by the specific attenuation Y, usually expressed in units of decibels per kilometer, related to the volume attenuation coefficient by where Y is in decibels per kilometer when γ is in inverse kilometers. The proportionality factor is 10 log10e. The specific attenuation for a given radar wavelength depends on the temperature and the drop-size distribution. If this distribution is known or can be approximated as a function of rainfall rate, the specific attenuation can be estimated as a function of rainfall rate.