Reynolds averaging
From Glossary of Meteorology
Reynolds averaging[edit | edit source]
An averaging procedure applied to variable quantities such as wind speed and temperature in a turbulent flow.
If the variable is 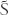 , the averaging procedure may be given by and
, the averaging procedure may be given by and 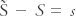 is the fluctuating part so that
is the fluctuating part so that  where S is the average value, s the fluctuating part, and the bar indicates the averaging process. The average is usually taken over a period of time but it may be taken over space or over an ensemble of realizations. This decomposition is called Reynolds averaging. Reynolds averaging has been applied to the Navier–Stokes equations to formulate, for example, turbulent fluxes and the turbulence kinetic energy equation. The drawback of this procedure is that it leads to the problem of turbulence closure.
where S is the average value, s the fluctuating part, and the bar indicates the averaging process. The average is usually taken over a period of time but it may be taken over space or over an ensemble of realizations. This decomposition is called Reynolds averaging. Reynolds averaging has been applied to the Navier–Stokes equations to formulate, for example, turbulent fluxes and the turbulence kinetic energy equation. The drawback of this procedure is that it leads to the problem of turbulence closure.

