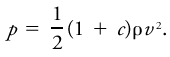Wind pressure
From Glossary of Meteorology
wind pressure
(Also called velocity pressure.) The total force exerted upon a structure by wind.
For a flat surface it consists of two factors, the first being the dynamic pressure exerted on the windward side of the surface (wind load). This is equal to (1/2)ρv2, where ρ is the air density and v is the wind speed normal to the surface. The second factor is the pressure decrease, or suction, produced on the leeward side of the surface, which is equal to (1/2)cρv2, where c is a structural constant varying from -0.3 for cylindrical objects to 1.0 for long plates. The wind pressure p is the sum of these two, or This formula should be used with caution. The actual wind pressure depends on the shape of the object and the nature of the environment. For objects not presenting a flat surface to the wind, such as bridges and chimneys, complicating aerodynamic factors are introduced that make the above formula invalid.