Potential
From Glossary of Meteorology
potential
- A function of space, the gradient of which is equal to a force.
In symbols,where F is the force, ∇ the del operator, and φ the potential. A force that may be so expressed is said to be "conservative," and the work done against it in motion from one given equipotential surface to another is independent of the path of the motion. In meteorology, the force of gravity has a potential, the geopotential, which, if the acceleration of gravity g is taken as constant, may be written φ = gZ, where Z is the height coordinate. The pressure force has in general no potential, nor do the Coriolis or viscous forces. By extension and analogy, the velocity potential, acceleration potential, and Gibbs function (thermodynamic potential) are defined.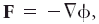
- Applied to the value that an atmospheric thermodynamic variable would attain if processed adiabatically from its initial pressure to a standard pressure, typically 100 kPa.
