Test2
From Glossary of Meteorology
- A-display
- 1. A radar display on test test test which targets appear as vertical deflections from a horizontal line that represents elapsed time from the most recent transmitted pulse.
- A/D converter
- 1. Abbreviation for analog-to-digital converter, an electronic device for quantifying a (typically) continuous-time voltage signal to a numeric discrete-sample sequence.
- AABW
- 1. Abbreviation for Antarctic Bottom Water.
- AAMW
- 1. Abbreviation for Australasian Mediterranean Water.
- ab-polar current
- 1. (Obsolete.) An air current moving away from either of the earth's poles.
- abatement
- 1. The lessening or reduction of an atmospheric state that is considered detrimental to humans, animals, plants, or structures.
- abbreviated ship code
- 1. An international code assigned to a ship to identify it as the source of meteorological observations.
- abduction
- 1. Development of a hypothesis to explain observations; frequently used in diagnostic expert systems; can lead to false conclusions.
- ABI
- 1. Abbreviation for Advanced Baseline Imager.
- abiotic
- 1. Refers to nonliving basic elements and compounds of the environment.
- ABL
- 1. Abbreviation for atmospheric boundary layer.
- ablation
- 1. #All processes that remove snow, ice, or water from a glacier, snowfield, etc.; in this sense, the opposite of accumulation.
- ablation area
- 1. That portion of a glacier surface below the firn line where ablation exceeds accumulation; the opposite of accumulation area.
- abnormality
- 1. In meteorology, a deviation of the weather or climate from the conditions normally expected at a particular time and place; a deviation from the normal.
- Abrolhos squalls
- 1. (Also called abroholos.) Rain or thundersqualls of the frontal type experienced mainly from May through August near the Abrolhos Islands (18°S) off the coast of Brazil.
- abscissa
- 1. The horizontal coordinate in a two-dimensional system of rectangular Cartesian coordinates; usually denoted by x; also, the horizontal axis of any graph.
- absolute
- 1. #With respect to atmospheric motions, refers to an absolute coordinate system; for example, absolute vorticity as distinguished from relative vorticity.
- absolute altitude
- 1. The true vertical distance above the terrain.
- absolute angular momentum
- 1. The angular momentum as measured in an absolute coordinate system; hence, the vector product of the position vector of a particle into the absolute momentum of the particle.
In the atmosphere the absolute angular momentum M per unit mass of air is equal to the sum of the angular momentum relative to the earth and the angular momentum due to the rotation of the earth:
where r is the distance from the center of the earth to the particle, u the relative eastward component of velocity, φ the latitude, and Ω the angular rotation rate of the earth. Since the earth's atmosphere is shallow, the variable r is often replaced by the constant a, defined as the radius of the earth. The absolute angular momentum per unit mass is then approximated by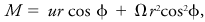
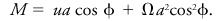
See angular-momentum balance, conservation of angular momentum.
- absolute annual range of temperature
- 1. The difference between the highest and lowest temperature observed at a location.
- absolute cavity radiometer
- 1. A combined electrical substitution and cavity radiometer where the electrical substitution inequivalence, efficiency of the cavity, the area of the entrance aperture, radiative and conductive losses, and other energy exchanges are accounted for such that the electrically substituted heating can be absolutely equated to the radiant heating of the detector.
- absolute coordinate system
- 1. (Or absolute reference frame.) The inertial coordinate system that has its origin on the axis of the earth and is fixed with respect to the stars.
- absolute drought
- 1. In British climatology, a drought period of at least 15 days during which no measurable daily precipitation has fallen.
- absolute extremes
- 1. Highest or lowest temperature observed over the whole period of observation.
- absolute humidity
- 1. Same as: vapor density
- absolute instability
- 1. #The state of a column of air in the atmosphere when it has a superadiabatic lapse rate of temperature (i.e., greater than the dry-adiabatic lapse rate).
An air parcel displaced vertically would be accelerated in the direction of the displacement. The kinetic energy of the parcel would consequently increase with increasing distance from its level of origin.
See parcel method, conditional instability, absolute stability.
- (Also called mechanical instability.) The state of a column of air in the atmosphere when its lapse rate of temperature is greater than the autoconvective lapse rate.
In such a column the air density would increase with elevation.
See also autoconvection.
- (Also called mechanical instability.) The state of a column of air in the atmosphere when its lapse rate of temperature is greater than the autoconvective lapse rate.
- absolute instrument
- 1. An instrument the calibration of which can be determined by means of simple physical measurements on the instrument.
- absolute isohypse
- 1. A line that has the properties of both constant pressure and constant height above mean sea level.
- absolute momentum
- 1. (Also called absolute linear momentum.) The (linear) momentum of a particle as measured in an absolute coordinate system; hence, in meteorology, the sum of the (vector) momentum of the particle relative to the earth and the (vector) momentum of the particle due to the earth's rotation.
- absolute monthly maximum temperature
- 1. Highest daily maximum temperature observed during a given calendar month over a specified period of years.
- absolute monthly minimum temperature
- 1. Lowest daily minimum temperature observed during a given calendar month over a specified period of years.
- Absolute Radiation Scale
- 1. [Abbreviated ARS; also referred to as the World Radiation Reference (WRR).] A radiation scale for measurement of solar exitance (irradiance).
- absolute refractive index
- 1. (Or absolute index of refraction.)
- absolute stability
- 1. The state of a column of air in the atmosphere when its lapse rate of temperature is less than the saturation-adiabatic lapse rate.
- absolute standard barometer
- 1. Barometer that provides absolute measurements of pressure without having to be calibrated.
For example, large sylphon barometers with optical reading have been a preferred type of primary or absolute standard barometer.
- absolute temperature extremes
- 1. Highest or lowest temperature observed over a specified period of observation used as a climatological record.
- absolute temperature scale
- 1. (Abbreviated A.)
- absolute velocity
- 1. Velocity as measured in an absolute coordinate system; hence, in meteorology, the (vector) sum of the velocity of a fluid parcel relative to the earth and the velocity of the parcel due to the earth's rotation.
The east–west component is the only one affected:
where u and ua are the relative and absolute eastward speeds, Ω the angular speed of the earth's rotation, r the radial distance of the parcel from the center of the earth, and φ the latitude of the parcel.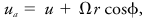
- absolute vorticity
- 1. #The vorticity of a fluid particle determined with respect to an absolute coordinate system.
The absolute vorticity vector is defined by 2Ω + ∇ × u, where Ω is the earth's angular velocity vector and u is the three-dimensional relative velocity vector.
- The vertical component η of the absolute vorticity vector (as defined above) given by the sum of the vertical component of the vorticity with respect to the earth (the relative vorticity) ζ and the vorticity of the earth (equal to the Coriolis parameter) f:

- The vertical component η of the absolute vorticity vector (as defined above) given by the sum of the vertical component of the vorticity with respect to the earth (the relative vorticity) ζ and the vorticity of the earth (equal to the Coriolis parameter) f:
- absolute zero
- 1. The zero point of the Kelvin temperature scale, of fundamental significance in thermodynamics and statistical mechanics.
- absorbance
- 1. Used mostly by chemists, the negative logarithm (base 10) of the transmittance of an absorbing sample, often corrected for reflection by its container.
- absorbed solar radiation
- 1. Solar radiation absorbed by the atmosphere's constituent gases, suspended material, clouds, or by the earth's surface.
- absorptance
- 1. One minus the sum of reflectance and transmittance.
- absorption
- 1. #The process in which incident radiant energy is retained by a substance.
- absorption band
- 1. A connected series of closely spaced or overlapping absorption lines.
- absorption coefficient
- 1. A measure of the extinction due to absorption of monochromatic radiation as it traverses a medium.
- absorption cross section
- 1. The area that, when multiplied by the irradiance of electromagnetic waves incident on an object, gives the radiant flux absorbed and dissipated by the object. Customary usage in radar describes the absorption cross section of an object as the area that, when multiplied by the power density of incident plane-wave radiation, gives the power absorbed and dissipated by the object.
- absorption hygrometer
- 1. (Sometimes called chemical hygrometer.) A type of hygrometer that measures the water vapor content of the atmosphere by means of the absorption of vapor by a hygroscopic chemical.
The query description has an empty condition.
